The Future of Data Centers: Strategic Investment Insights for Operators and Capital Providers
Table of Contents
I. Introduction
II. Investment Landscape and Strategic Partnerships
1. The Equinix, GIC, and CPP Investments Trio: $15 Billion Strong
2. Blackstone's Bold $16.1 Billion Bet on AirTrunk
3. Digital Realty and Blackstone's $7 Billion Hyperscale Gambit
4. The $30 Billion AI Infrastructure Fund: A BlackRock, Global Infrastructure Partners, Microsoft, and MGX Tour de Force
5. The Through Line: Visionary Partnerships Redefining the Data Center Landscape
III. The Strategic Importance of Data Center Assets in Investment Portfolios
1. Stable Cash Flow from Long-Term Contracts
2. Substantial Growth Potential
3. Inflation Hedge and Pricing Power
4. Technological Alignment with AI and High-Performance Computing
5. Significance in Investment Portfolios
IV. Investor Hurdles: Cyclical Leasing Patterns in Data Centers & Navigating Hyperscaler Demand
1. Leasing Surges Driven by Hyperscaler Growth
2. The "Digestion" Phase
3. Strategic Implications for Data Center Operators
4. Key Takeaway for Investors
V. Geographic Diversification and Secondary Market Potential
1. Avoiding High Competition and Cost in Primary Markets
2. Reduced Grid Constraints and Regulatory Flexibility
3. Cost Advantages and Untapped Demand
4. Take for Take Comparison: Primary and Secondary Data Center Markets
VI. Embracing Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
1. Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): A Stable, On-Site Power Solution
2. Microreactors: Flexible Power for Remote and Off-Grid Centers
3. Tackling Challenges and Scaling for the Future
4. Strategic Considerations for Scaling Energy
5. Energy Consumption and Sustainable Development in Data Centers
VII. Strategic Implications of Edge Computing, 5G, and AI in Data Center Investments
1. Integration of Edge Computing and 5G
2. Integration of AI and Predictive Management
3. Strategic Insight
VIII. Investment Recommendations for Maximizing Returns
1. Prioritize Edge Data Centers in Growth Regions
2. Invest in AI-Enabled Facilities
3. Emphasize Modular and Sustainable Infrastructure
4. Support 5G-Edge Synergy
5. Forward-Looking Perspective
IX. Data Centers by the Numbers: A Macro Perspective with Tailwinds for Investment
1. Escalating Data Generation: Fuel for Expansion
2. AI's Growing Computational Needs: The Engine of Future Infrastructure
3. Cloud Computing Expansion: A Massive Industry Shift
4. Content Creation Surge: A Digital Economy Phenomenon
5. Emerging Markets and IoT Growth: New Frontiers of Data Demand
6. A Macro Investment Play with Resilience and Growth Potential
X. Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives for Data Center Investment and Growth
1. Stable and Predictable Returns
2. Growth Potential Driven by Technological Demand
3. Technological Alignment with Emerging Needs
4. Commitment to Sustainability
5. Strategic Recommendation: Aligning with Technological Convergence and Sustainability
I. Introduction
In an era where digital transformation is accelerating at an unprecedented pace, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and data-intensive applications, data centers have become the backbone of modern infrastructure. For data center operators and capital providers, understanding the evolving landscape is crucial for strategic investment and operational success. This report delves into recent investment trends, the strategic significance of data centers in diversified portfolios, and the converging forces of edge computing, 5G, and AI that are reshaping the sector.
II. Investment Landscape and Strategic Partnerships
In the blink of an eye, the data center infrastructure has tallied $107.5 billion (excluding multiple undisclosed commitments) at least, for the frenetic 2023-2024 period. This staggering investment frenzy underscores the industry's tantalizing twin promises: scalability and sustainability. As AI and cloud computing continue their relentless march, strategic partnerships are being forged with a mix of real estate savvy and operational wizardry. Let's take a closer look at the heavy-hitters:
The Equinix, GIC, and CPP Investments Trio: $15 Billion Strong
Their brainchild, the xScale Hyperscale Platform, is all about delivering bespoke AI and cloud solutions to the who's who of digital markets across the U.S., Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Think of it as a masterclass in addressing the intricacies of each region.
By planting their flag in regions on the cusp of a digital explosion, this partnership is poised to reap the rewards of a carefully orchestrated geographic diversification strategy.
Blackstone's Bold $16.1 Billion Bet on AirTrunk
With its acquisition of AirTrunk, the Asia-Pacific's undisputed data center champion, Blackstone has firmly entrenched itself in the region's burgeoning markets—Australia, Japan, and Singapore, to name a few. These countries are hurtling towards a digital future at breakneck speed.
AirTrunk's facilities, designed with the future in mind, boast AI-ready infrastructure that's perfectly in sync with Blackstone's forward-thinking ethos.
Digital Realty and Blackstone's $7 Billion Hyperscale Gambit
Their joint venture is headlined by four heavyweight data centers, collectively packing a 500 MW punch, strategically scattered across Frankfurt, Paris, and Virginia. This is a deliberate play to satiate the insatiable appetite of the AI and cloud services market.
By doubling down on established hubs in Europe and North America, the duo is making a concerted effort to stay ahead of the curve in high-density computing and AI processing.
The $30 Billion AI Infrastructure Fund: A BlackRock, Global Infrastructure Partners, Microsoft, and MGX Tour de Force
Launched in the waning days of September 2024, this monumental fund is an unapologetic bet on the future of AI-driven data center infrastructure, with sustainability firmly in its crosshairs.
As the fund's resources are allocated to cutting-edge data centers in Abu Dhabi, the U.S., and beyond, the stage is set for a revolution in fields like finance and healthcare, all while harnessing the power of edge computing, real-time analytics, and renewable energy.
The Through Line: Visionary Partnerships Redefining the Data Center Landscape
Each of these partnerships, in its own unique way, embodies a thoughtful, almost intuitive approach to navigating the data center sector's uncharted territories. By placing big bets on AI, cloud services, and sustainable tech, these trailblazers are, in effect, scripting the industry's next chapter.
III. The Strategic Importance of Data Center Assets in Investment Portfolios
Data centers offer unique benefits that make them highly attractive additions to diversified portfolios. Their crucial role in the digital economy positions them as stable, scalable, and adaptable assets, aligning seamlessly with the broader shifts in technology and the escalating demand for data.
1. Stable Cash Flow from Long-Term Contracts
Data centers typically engage in multi-year contracts that often include renewal options and built-in rate escalations. These agreements provide reliable revenue streams, essential for generating predictable cash flows. This stability appeals to investors because it mirrors the resilience of traditional real estate assets but with the added advantage of being integral to the indispensable digital infrastructure of modern economies.
The strong commitments from cloud service providers, Software as a Service (SaaS) companies, and hyperscalers help maintain high occupancy rates and reduce vacancy risks. This consistent demand reinforces stability in cash flows over the long term. Industry leaders underscore the sustained growth and reliability in this sector by further positioning their capital in the sector.
2. Substantial Growth Potential
Global data traffic is projected to increase by nearly 24% annually, driven by surging content creation, AI processing needs, cloud expansion, and the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. As we advance into the era of AI and advanced machine learning, there's a high demand for data centers capable of supporting high-performance computing (HPC) and GPU-based infrastructures.
According to leading estimates, the global data center market is expected to grow from $360 billion in 2024 to $550 billion by 2027, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16%. This rapid expansion is linked to various sectors that rely heavily on digital infrastructure—from autonomous vehicles to smart cities—all dependent on local data processing and low-latency connections provided by data centers.
3. Inflation Hedge and Pricing Power
Data centers offer unique flexibility in their pricing structures, often featuring lease agreements with inflation-indexed escalators. This mechanism allows operators to adjust pricing in line with inflation, ensuring that returns remain resilient even during periods of rising costs.
With an increased focus on sustainability, some operators are implementing dynamic pricing for energy-efficient facilities. This strategy not only attracts tenants who prioritize Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria but also enables operators to pass on utility savings while staying competitive. Reports from Data Center International and IDC highlight these evolving pricing strategies within the industry.
4. Technological Alignment with AI and High-Performance Computing
As the demand for AI and machine learning accelerates, data centers catering to these high-performance workloads gain a significant competitive edge. AI applications are expected to heighten data center requirements for both power and cooling, making AI-ready facilities with GPU-equipped infrastructure a rapidly growing segment in digital assets.
This technological alignment ensures that data centers remain critical infrastructure for tech companies, healthcare providers, financial services, and manufacturing sectors—all increasingly relying on AI to drive operational efficiency and innovation. Industry insights from the Dell'Oro Group emphasize the importance of this synergy between data centers and emerging technologies.
5. Significance in Investment Portfolios
Data centers are compelling assets for investment portfolios not only due to their market growth and adaptability but also because they address key investor concerns like stability, inflation protection, and technological advancement. They blend the predictability of real estate investments with the exponential growth potential of the tech sector, creating balanced, high-potential assets capable of yielding sustainable long-term returns.
By investing in data centers, portfolios gain a hedge against traditional market volatility while positioning themselves to benefit from the transformative impact of AI, edge computing, and 5G technologies—all of which demand robust and scalable digital infrastructure.
IV. Investor Hurdles: Cyclical Leasing Patterns in Data Centers & Navigating Hyperscaler Demand
The leasing dynamics in data centers are heavily shaped by hyperscale cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, which together drive over half of the leasing demand in major markets. Their approach to leasing—large, concentrated blocks of space—creates distinct cycles of heightened activity followed by quieter periods. This cyclical pattern affects leasing dynamics, absorption rates, and revenue stability for data center operators.
1. Leasing Surges Driven by Hyperscaler Growth
Leasing demand from hyperscalers tends to spike in response to factors such as expanding AI applications, increasing cloud service needs, or major product launches. In recent years, hyperscale demand has soared, with U.S. hyperscale leasing alone accounting for roughly 700 MW in 2023. These surges can occur rapidly, with a single hyperscaler like Amazon Web Services leasing over 100 MW in Northern Virginia within a short timeframe. This kind of large-scale leasing drives major peaks in primary markets; for instance, in Frankfurt, hyperscaler demand has reached up to 60% of total leasing activity, and in São Paulo, hyperscaler-led demand has grown by 50% over the last two years.
2. The "Digestion" Phase
Following these leasing surges, hyperscalers often enter a “digestion” phase, during which they integrate and optimize newly acquired capacity. During these phases, leasing activity can drop significantly—often by 40-50%. In Northern Virginia, the world’s largest data center market, leasing demand notably slowed after a record-breaking period in 2022. This pause can last from several months to over a year, depending on hyperscaler expansion schedules and overall market conditions. In markets like Querétaro, the post-surge slowdown was even more pronounced, with leasing activity nearly halting after a period of rapid growth.
3. Strategic Implications for Data Center Operators
For operators and investors, managing these cycles requires a keen understanding of hyperscaler demand patterns and strategic portfolio diversification. In North America, where some operators report that 60-70% of their leasing is tied to hyperscalers, the cyclical nature of this demand can introduce significant volatility in occupancy rates. To manage this risk, successful operators often balance their hyperscale business with enterprise customers, whose leasing demand is typically more consistent throughout the year.
4. Key Takeaway for Investors
Recognizing these cyclical patterns in hyperscaler leasing can help investors align their strategies with the predictable surges and digestion phases that define this market. A well-timed investment approach, combined with a balanced portfolio that captures hyperscaler growth without overexposure to demand fluctuations, can create greater stability and long-term value for stakeholders.
V. Geographic Diversification and Secondary Market Potential
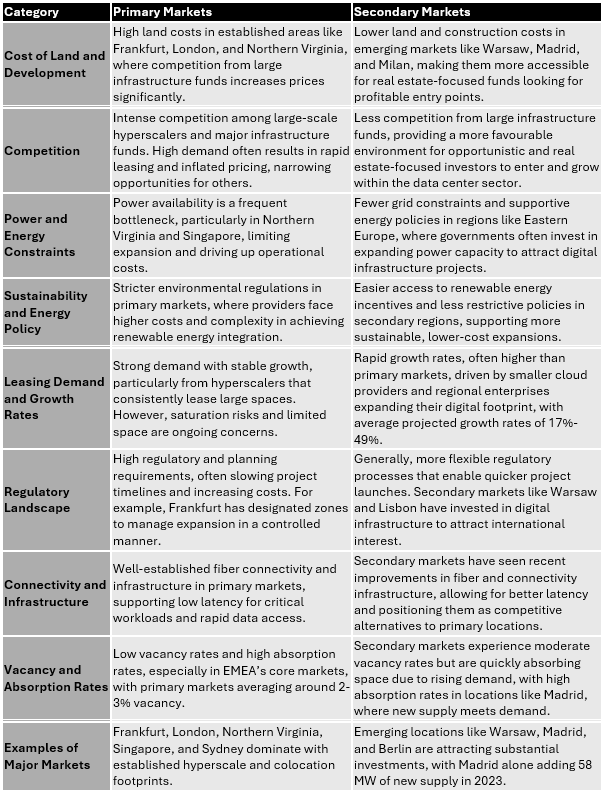
Expanding into secondary data center markets has become an attractive strategy for opportunistic and real estate-focused funds, especially as major infrastructure funds, equipped with lower cost of capital, have increasingly pushed prices higher in primary hubs in UK/Europe like Frankfurt, London, Amsterdam, and Paris (FLAP). Here’s how secondary markets are emerging as viable alternatives and the competitive advantages they offer:
1. Avoiding High Competition and Cost in Primary Markets
Competition with Lower-Cost Capital: Infrastructure funds, which typically have access to lower-cost capital, are able to outbid more opportunistic funds in core data center markets. This leads to higher land and facility prices, squeezing returns for traditional real estate funds. Secondary markets, however, experience less competition from these infrastructure giants, making them a more viable and cost-effective choice for investors seeking to enter the data center space with favorable acquisition costs.
Example of Strategic Shifts: Apto, partnering with PIMCO on a €1 billion data center fund, is investing in cities like Athens, Madrid, and Milan. These locations offer strategic advantages, including regulatory flexibility, lower land prices, and infrastructure investments that are accommodating the rise in data demand. This move underscores the appeal of secondary markets, where infrastructure and regulatory conditions create more favorable returns for real estate-driven investment approaches.
2. Reduced Grid Constraints and Regulatory Flexibility
Grid and Power Supply Advantages: Many secondary markets have fewer grid limitations and more flexible energy policies, which makes expansion smoother and less costly than in congested hubs. For instance, regions in Southern and Eastern Europe are actively upgrading power infrastructures to accommodate data centers without the delays often seen in FLAP markets, where grid capacity is increasingly constrained. As governments in these regions seek to attract digital infrastructure, they often provide incentives for renewable energy usage and power distribution improvements.
Supportive Regulatory Frameworks: Cities like Warsaw and Lisbon are gaining traction as they offer streamlined regulatory processes and are investing in digital infrastructure. For example, Poland’s government is ramping up initiatives to expand grid capacity specifically for data centers, making it a practical choice for investors seeking growth markets without the typical regulatory hurdles of core data center hubs.
3. Cost Advantages and Untapped Demand
Better Land Basis and Development Costs: Secondary markets generally have lower land and development costs, making them ideal for funds aiming to maximize return on investment. In regions like Milan and Madrid, land is more affordable, allowing investors to secure larger plots for future expansions, which would be challenging in space-constrained FLAP areas. This lower land cost directly impacts returns, as initial capital expenses remain lower while demand grows.
Targeting Under-Served Demand: Secondary markets are also experiencing rising demand, as many of these regions are underserved in terms of local data capacity. Demand drivers include smaller cloud providers, regional enterprises, and governments moving toward digitization. For example, Madrid saw data center leasing growth of over 25% in 2023, driven by cloud expansion and lower costs compared to Western European hubs.
4. Take for Take Comparison: Primary and Secondary Data Center Markets
VI. Embracing Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Embracing Nuclear Power for Sustainable Data Center Energy
As data centers face soaring energy needs and growing environmental expectations, many are turning to nuclear power as a promising solution. With demand driven by AI, cloud computing, and digital expansion, companies are exploring innovative nuclear technologies, like small modular reactors (SMRs), to meet their energy needs sustainably.
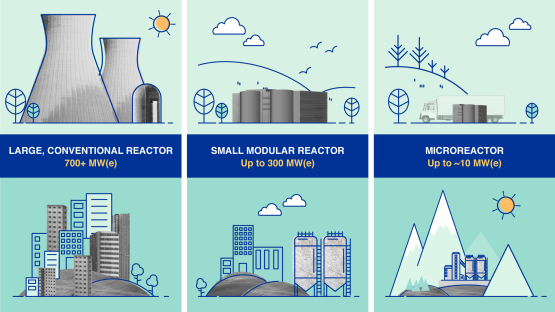
1. Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): A Stable, On-Site Power Solution
SMRs are compact, scalable reactors designed to provide a reliable energy source right where it’s needed, making them a game-changer for data centers looking to avoid the limitations of traditional power grids. Major companies like Google and Oracle are now exploring SMRs to meet the power needs of their large-scale operations.
• Less Reliance on the Grid: With SMRs, data centers gain a stable power source that’s independent of grid fluctuations and fuel price changes. Google, for instance, has partnered with Kairos Power to develop reactors capable of generating up to 500 MW by 2030, specifically to support its data centers. Oracle, meanwhile, plans to use three SMRs to power a new 1 GW facility, setting a strong precedent for the shift toward nuclear-powered data operations.
• A Clean, Reliable Energy Source: SMRs provide a steady, carbon-free power supply, giving data centers more control over their energy sources. This autonomy supports both operational stability and long-term sustainability goals. While large-scale SMR deployment is expected over the next decade, pilot projects are already in motion, as companies work with regulators to bring this innovative energy solution closer to reality.
Small modular reactors (SMRs) have a power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit. Many SMRs, which can be factory-assembled and transported to a location for installation, are envisioned for markets such as industrial applications or remote areas with limited grid capacity. (Image: A. Vargas/IAEA)
2. Microreactors: Flexible Power for Remote and Off-Grid Centers
Microreactors, such as the Westinghouse eVinci model, are an even smaller nuclear solution, ideal for data centers located in areas where grid power is less reliable or unavailable. Their size and adaptability make them highly suitable for smaller or modular data centers.
• Compact and Adaptable Power: Generating around 5 MW, these reactors can power smaller data centers or modular setups, especially in areas with limited grid access. This flexibility allows operators to expand sustainably into underserved areas without relying on conventional power sources.
• Case Study – Microsoft’s Commitment to Nuclear: Microsoft is making strides with nuclear power, creating a dedicated team to integrate SMRs and microreactors and signing agreements to power its Virginia facilities with nuclear energy. These efforts not only help lower its carbon footprint but also support the high energy demands of its advanced AI applications. Microsoft’s investments are paving the way for a new approach to energy in data centers, focused on both sustainability and performance.
3. Tackling Challenges and Scaling for the Future
Despite the clear benefits, nuclear power for data centers comes with regulatory hurdles and initial setup costs. Permitting and compliance are significant factors, and construction costs remain high. Yet, with increasing recognition of nuclear power’s potential for clean, stable energy, the path to adoption is likely to accelerate.
• A Scalable Solution for Growing Demands: As AI and data processing requirements outstrip traditional grid capabilities, nuclear energy presents a viable, scalable solution. Particularly in areas with supportive policies, nuclear power could offer data centers a way to keep pace with growing energy needs while maintaining environmental standards.
By adopting nuclear solutions like SMRs and microreactors, data centers are setting a new standard for sustainable energy management. Moving away from grid dependency, these centers are embracing a cleaner, more reliable energy future, positioning themselves as leaders in both innovation and environmental responsibility.
4. Strategic Considerations for Scaling Energy
The capacity constraints on traditional grids—especially in Europe and specific regions with dense hyperscale data center deployments—mean that sustained growth will increasingly rely on integrating nuclear power, renewables, and advanced grid infrastructure. Countries like Ireland and Denmark, where data center energy demand is expected to rise to nearly 30% and 15% of national electricity by 2028 and 2030, respectively, are already adjusting grid policies to accommodate sustainable energy sources that match the continuous power needs of data centers.
This trend underscores the importance of scaling both renewable (solar, wind) and nuclear (such as SMRs and microreactors) energy sources to address data centers’ future power requirements sustainably and avoid straining existing grid resources.
5. Energy Consumption and Sustainable Development in Data Centers
While demand for AI, cloud computing, and heavy data processing is growing, it means that data centers are consuming more and more energy.
In 2024, these facilities consume roughly 380 TWh of electricity, but this may grow to up to 620 TWh by 2030. While currently taking about 1-2% of worldwide electricity consumption, data centers may start representing 2.5% to 3% by the end of the decade. This huge growth represents a pressing need for fresh and environmentally friendly energy procedures across the industry.
• Transition to Renewable Energy - 2025-2027:
Large players like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft have been leading the charge in serious investments into renewable energy through the signing of Power Purchase Agreements for wind and solar sources. These agreements have been able to help them reduce their environmental footprint and cut energy costs by 15-30% compared to traditional grid costs. A number of people believe that, by 2025-2027, most large-scale data centers will be run mainly on renewable energy, consequently reducing most of the operational costs and environmental impacts.
• Exploring Nuclear Solutions: Small Modular Reactors and Microreactors Early 2030s
Looking ahead, some data centers are considering nuclear options that would provide a stable, low-carbon power supply. Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) can supply between 50-300 megawatts, microreactors from 1-5 MW: suitable solutions for facilities of all sizes. Each could replace an estimated 0.8 million tons of CO₂ emissions per year by providing an alternative to fossil fuels. Early projects by companies such as Microsoft and Oracle suggest that wider deployment of these reactors could start during the early 2030s, continuously and reliably powering huge data centers.
• Efficiency Gain through Advanced Cooling
It is estimated that about 35-45% of the energy usage in a data center is consumed by its cooling system alone. With more innovative technologies, such as liquid cooling, up to 40% less cooling energy use could be achieved. Advanced solutions in implementing these cooling technologies can reduce overall energy costs by 14-18%, thus allowing data centers to meet their carbon reduction targets.
VII. Strategic Implications of Edge Computing, 5G, and AI in Data Center Investments
The convergence of edge computing, 5G, and AI is reshaping the data center landscape, creating new investment opportunities and operational demands. As data needs continue to grow, the changes in infrastructure design and functionality are enabling data centers to meet the low-latency, high-compute demands required by real-time applications.
1. Integration of Edge Computing and 5G
• Real-Time Processing: Edge computing has emerged in response to the need for real-time processing in applications that demand ultra-low latency. Unlike traditional data centers, edge facilities process data closer to end-users, supporting sectors like autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare, and smart cities. By reducing data transmission times, edge data centers enhance user experience and allow for real-time decision-making in these sectors.
• 5G Expansion: The development of 5G, with its ultra-low latency and high-speed data transfer capabilities, complements edge computing by enabling high-bandwidth applications. This 5G-edge combination is essential for industries needing instant data exchange, from AR and VR in gaming to predictive maintenance in industrial settings. These applications generate massive data flows, making distributed data centers critical to maintaining seamless connectivity.
• Investment Opportunities: The global edge data center market is expected to reach $317 billion by 2026, driven by the need for local processing and low-latency capabilities. Companies like AtlasEdge and Liberty Global exemplify the potential of edge investments, operating over 100 edge locations across Europe to support digital-first industries with low-latency services. This growing demand for local infrastructure opens significant opportunities for investors in a high-growth sector, enabling real-time data processing at the local level.
2. Integration of AI and Predictive Management
• Operational Efficiency: AI is transforming operational efficiency in data centers through predictive analytics, which can forecast equipment failures, reduce downtime, and optimize energy consumption. As data centers run continuously to support AI, cloud, and real-time applications, operational resilience becomes a key focus for investors.
• High-Performance Computing: As AI workloads grow in complexity and scale, the demand for GPU-based configurations and high-performance computing systems has increased dramatically. Data centers are adapting to support these demands by incorporating advanced cooling and power systems to manage the intense computational requirements of AI applications, such as deep learning and natural language processing. The need for AI-compatible infrastructure is rising sharply, as Machine Learning applications generate unprecedented data loads. High-density computing resources like GPUs and TPUs, along with advanced cooling systems, are essential for managing the heat produced by continuous, high-power processing.
For instance, Google’s AI-driven cooling system has reduced cooling costs by 40%, showcasing the operational efficiency gains possible through AI optimization. AI-enabled data centers represent a promising investment opportunity, appealing to clients in technology, finance, and healthcare who need intensive computation capabilities. With enhanced operational resilience and cost efficiencies, these facilities align with investor demand for high-growth, sustainable assets.
3. Strategic Insight
As edge computing, 5G, AI, and sustainability converge, the data center investment landscape is transforming, positioning data centers as essential assets within the digital economy. Diverse portfolios that address real-time data processing needs, energy efficiency, and scalable operations are poised for long-term growth and resilience. Edge and AI-ready data centers, in particular, offer attractive opportunities for investors seeking stability and growth in an increasingly digital world.
VIII. Investment Recommendations for Maximizing Returns
1. Prioritize Edge Data Centers in Growth Regions
• Focus Areas: Emerging markets in APAC and MENA are seeing rapid 5G adoption and require edge computing infrastructure to support local data processing. These regions are forecasted to experience substantial growth in edge data centers due to the rising demand for low-latency applications like IoT and augmented reality.
• Rationale: Edge data centers, when combined with 5G, dramatically reduce latency and provide real-time data processing, which is vital for sectors such as healthcare, retail, and transportation in densely populated urban areas. In APAC, the edge data center market alone is anticipated to grow by over 14.8% annually, creating lucrative opportunities for investors to capitalize on local demand for low-latency data infrastructure.
2. Invest in AI-Enabled Facilities
• Focus Areas: Target data centers equipped for predictive management and AI-specific workloads, such as those supporting machine vision, natural language processing, and other generative AI applications.
• Rationale: AI integration is reshaping data center design. Facilities that can support AI tasks demand high-density processing power, advanced cooling systems, and efficient energy use to handle increased workloads. AI-specific facilities can reduce costs by using predictive algorithms to manage resource allocation, which allows for more efficient power consumption and space utilization. As the AI-driven edge market expands, investors focusing on AI-enabled facilities are well-positioned to benefit from the need for local, data-intensive processing capabilities.
3. Emphasize Modular and Sustainable Infrastructure
• Focus Areas: Modular facilities in Europe and North America are already aligned with ESG goals and regulatory demands, but demand is extending globally as modular data centers are increasingly adaptable, affordable, and scalable.
• Rationale: Modular designs are ideal for distributed edge locations where rapid deployment and scalability are critical. They allow operators to deploy units quickly and sustainably while reducing environmental impact by integrating fuel cells, solar panels, and battery storage for a clean, uninterrupted power supply. Investments in modular infrastructure can provide long-term resilience, especially with technologies like solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) offering 24/7 clean energy generation that aligns with ESG goals and regulatory expectations.
4. Support 5G-Edge Synergy
• Focus Areas: Facilities near urban centers with high-density 5G infrastructure offer high returns as they are equipped to meet low-latency, high-bandwidth demands essential for IoT and mobile applications.
• Rationale: The convergence of 5G and edge computing in urban centers enables real-time data transfer, unlocking advanced applications in smart cities and autonomous systems. This synergy is particularly transformative for industries like logistics and healthcare, where instant data processing is crucial. Investment in facilities optimized for 5G-edge synergy allows for the seamless delivery of next-gen applications, potentially attracting both enterprise clients and hyperscalers.
5. Forward-Looking Perspective
As 5G, AI, and edge computing continue to converge, data centers will evolve into distributed networks of high-efficiency, modular facilities supporting localized, high-performance computing needs. Investors who strategically position their assets to support this convergence will not only capitalize on emerging technological needs but will also drive sustainable growth aligned with regulatory and environmental goals. A future-focused strategy emphasizes the resilience, adaptability, and sustainability of data centers—making this a prime period for data center investments in dynamic and rapidly developing markets.
IV. Data Centers by the Numbers: A Macro Perspective with Tailwinds for Investment
The data center industry is positioned as a resilient, macro-level investment opportunity. Driven by unprecedented data generation, the expansion of AI, cloud adoption, and growth in content creation and IoT, data centers are indispensable to the digital economy. This growth offers a compelling case for investors, with numerous factors acting as tailwinds to drive the sector forward.
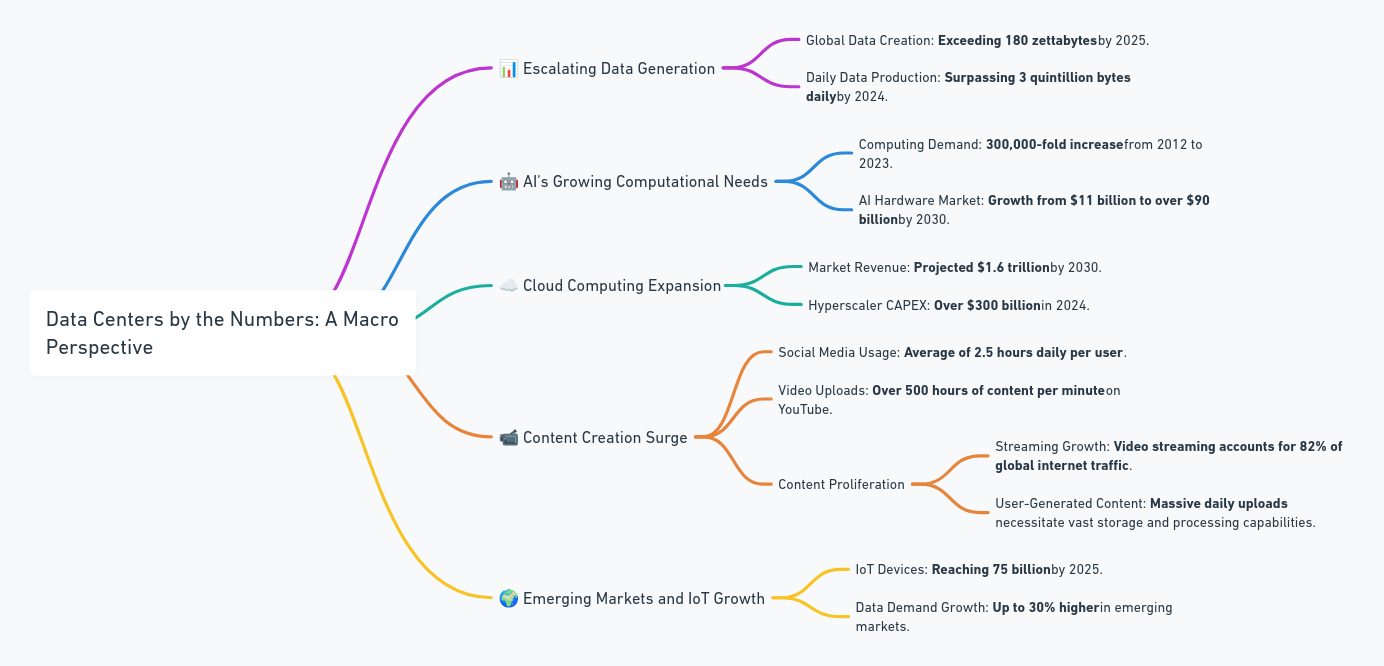
1. Escalating Data Generation: Fuel for Expansion
Global Data Creation: As the digital world expands, global data creation is set to surpass 180 zettabytes by 2025—equivalent to trillions of terabytes. With IoT sensors, mobile devices, and digital platforms fueling constant data production, the demand for storage and processing power is soaring.
Daily Data Production: By 2024, over 3 quintillion bytes of data will be generated daily, underscoring the vast scale at which data centers are becoming essential to manage and store this information. This explosive growth supports data centers as a long-term investment, with a nearly insatiable demand for capacity and processing speed.
Investment Insight: This data boom is both global and accelerating, providing a steady pipeline of demand that shields the data center industry from short-term fluctuations. For investors, the scale of data creation alone ensures an expanding market that will rely heavily on advanced data centers.
2. AI's Growing Computational Needs: The Engine of Future Infrastructure
Exponential Computing Demand: Since 2012, computing requirements for AI have skyrocketed by a 300,000-fold increase, driven by advances in deep learning, neural networks, and generative models like GPT and large language models. This escalation demands cutting-edge hardware and optimized data center design to handle processing at scale.
AI Hardware Market Growth: AI hardware, including GPUs and TPUs, is expected to grow from $11 billion to over $90 billion by 2030. This hardware growth reflects AI’s insatiable need for more processing power, while AI-driven workloads necessitate data centers that can support intensive, high-density computing.
Investment Insight: AI is not just a growth market; it is reshaping data infrastructure, transforming data centers into specialized environments that can accommodate high-performance computing. Investing in data centers is effectively investing in the backbone of AI, which is projected to expand across industries, from healthcare to finance to entertainment.
3. Cloud Computing Expansion: A Massive Industry Shift
Market Revenue Growth: Cloud computing revenue is set to exceed $1.6 trillion by 2030, as businesses migrate from on-premises solutions to scalable, cloud-based platforms. Data centers are integral to this shift, serving as the physical infrastructure that supports cloud operations.
Hyperscaler CAPEX: In 2024, hyperscalers like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google are expected to invest over $300 billion in capital expenditures, much of it in expanding data center infrastructure. This high CAPEX allocation is essential to meet rising cloud service demand and to expand network reach and service capacity.
Investment Insight: The cloud is now a core service across nearly every industry. For investors, data centers dedicated to cloud operations represent high-demand, low-risk assets that are critical to supporting the continued growth of global digital infrastructure.
4. Content Creation Surge: A Digital Economy Phenomenon
Social Media Usage and Video Uploads: Users spend an average of 2.5 hours daily on social media, and platforms like YouTube see over 500 hours of content uploaded per minute. This surge in user-generated content, particularly video, underscores the need for vast storage and processing capabilities.
Streaming Dominance: Video streaming now accounts for 82% of global internet traffic, driven by platforms like Netflix, YouTube, and Twitch. This proliferation means data centers must support rapid data delivery and significant storage capacity to meet streaming demands.
Investment Insight: Content creation, especially video, drives high and consistent data throughput requirements. Data centers, therefore, represent a strong investment for managing the exponential increase in streaming and social media usage globally.
5. Emerging Markets and IoT Growth: New Frontiers of Data Demand
IoT Device Explosion: By 2025, IoT devices will reach 75 billion, contributing to a vast web of interconnected data points. These devices create significant data volumes that need to be processed in real time, making edge data centers essential for reducing latency.
Higher Data Demand in Emerging Markets: Emerging economies, particularly in APAC and MENA, are seeing up to 30% higher data demand growth than developed regions, spurred by urbanization and the digital transformation of industries.
Investment Insight: Emerging markets present a unique growth opportunity as IoT and digital services expand rapidly. Investing in edge data centers in these regions supports real-time processing closer to the data source, capitalizing on high demand with lower operating costs.
A Macro Investment Play with Resilience and Growth Potential
With data generation, AI, cloud, content creation, and IoT all expanding, the data center industry enjoys strong and sustainable tailwinds. These trends make data centers a foundational asset class in the digital economy, offering investors not only growth but a high degree of stability against market volatility. The infrastructure required to sustain our digital world positions data centers as a safe and forward-looking investment in an increasingly digital and data-driven society.
X. Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives for Data Center Investment and Growth
Data centers, positioned at the heart of digital transformation, offer a compelling combination of stable returns, growth potential, technological alignment, and sustainability. Given the accelerating shift to digital, data centers are fast becoming essential infrastructure for a digital-first world. Here’s an expanded view on why this space holds strong investment potential and how strategic alignment in key areas can maximize growth opportunities:
1. Stable and Predictable Returns
Long-Term Contracts and High Demand Resilience: Data centers generate reliable, recurring revenue through multi-year contracts with large enterprises, hyperscalers, and cloud providers. This contractual foundation ensures predictable cash flows, reducing exposure to economic cycles. Data centers serve as critical infrastructure for modern enterprises, with demand largely unaffected by economic downturns as data consumption and digital services remain essential in all climates.
High Entry Barriers and Durable Value: The data center market is capital-intensive, requiring specialized technology, infrastructure, and regulatory compliance. These high entry barriers protect existing operators from new competition and add long-term stability. In a world where 24/7 digital access is essential, data centers offer investors a durable asset class with low risk, positioning them as a safer, long-term play compared to traditional real estate.
Investment Insight: The combination of contractual revenue streams, essential services, and high barriers to entry provides data centers with unique stability, making them attractive for investors seeking dependable returns in a volatile economy.
2. Growth Potential Driven by Technological Demand
Exponentially Growing AI and Cloud Markets: Data center growth is underpinned by the rapid expansion of AI, cloud computing, and data-intensive applications. AI's rise alone has spurred unprecedented demand for processing power, with computing requirements increasing by a 300,000-fold from 2012 to 2023. Cloud adoption continues to climb, projected to drive global revenue to $1.6 trillion by 2030. Hyperscalers, in particular, are forecasted to invest over $300 billion in data center infrastructure this year to expand capacity for emerging applications.
Edge and 5G Demand: As 5G spreads globally, it enables edge data centers to meet low-latency requirements for real-time applications, from autonomous vehicles to augmented reality. These technologies amplify demand for localized data processing facilities, which are often less expensive and quicker to deploy than centralized data centers, driving a new phase of growth in digital infrastructure.
Investment Insight: With AI and cloud adoption showing no signs of slowing, data centers remain at the center of digital infrastructure growth. By positioning investments in facilities aligned with AI, cloud, and edge computing needs, investors capture significant, scalable demand for the foreseeable future.
3. Technological Alignment with Emerging Needs
Supporting Advanced Technologies: Data centers increasingly need to handle high-performance computing and low-latency data transfers essential for AI and 5G applications. Facilities are integrating specialized hardware like GPUs and TPUs for machine learning workloads, along with high-speed network equipment to support 5G-enabled applications. These capabilities make data centers indispensable to technology’s most cutting-edge advancements.
Edge Synergy: Edge computing decentralizes data processing, bringing it closer to end-users for applications that require immediate data access. This shift allows data centers to support IoT devices, IIoT applications, and real-time analytics, transforming industries like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. The symbiotic relationship between edge computing and data centers enables rapid responses to data demands, accommodating everything from predictive maintenance to advanced robotics.
Investment Insight: Data centers that support edge computing, 5G, and AI integration align with the future needs of technology-driven industries. By investing in data centers optimized for advanced processing and low latency, investors tap into a future-ready infrastructure critical to industry innovation.
4. Commitment to Sustainability
Regulatory and ESG Compliance as Necessities: Growing environmental regulations and ESG pressures make sustainability a priority. Data centers consume significant energy, with global electricity demand for the sector projected to reach 620 TWh by 2030. To meet ESG and regulatory requirements, data centers are increasingly turning to renewable energy sources, efficient cooling methods, and energy management systems. Government incentives and public policies favoring sustainable infrastructure further enhance the sector’s investment appeal.
Integration of Clean Energy Solutions: Innovative technologies like solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), modular microgrids, and sustainable power storage are making it possible for data centers to meet 24/7 operational demands with reduced environmental impact. By decentralizing energy production, adopting microgrids, and using high-efficiency cooling systems, data centers are pioneering green solutions that not only lower costs but also support long-term environmental goals.
Investment Insight: As environmental pressures increase, data centers adopting sustainable practices are becoming preferred choices for ESG-focused investors. Facilities that incorporate renewable energy, sustainable architecture, and advanced cooling technologies position themselves to capitalize on both regulatory incentives and societal shifts towards sustainability.
Strategic Recommendation: Aligning with Technological Convergence and Sustainability
Data centers represent a convergence of stability, scalability, and adaptability. Investors are urged to focus on facilities that:
Leverage Edge Computing: Edge facilities in urban centers allow for distributed, low-latency data processing, essential for IoT and real-time applications.
Integrate 5G Capabilities: High-speed, high-bandwidth data centers support the next generation of 5G-powered technologies.
Enable High-Density AI Processing: Facilities equipped with specialized hardware and advanced cooling for AI applications address the demand for powerful, efficient computation.
Adopt Sustainable Practices: Green building practices, renewable energy, and efficient cooling systems align with ESG goals and support long-term viability.
With these strategic imperatives, data center investments align with the expanding demands of a digital economy, providing resilience, high growth potential, and a path toward sustainable profitability. This focus on advanced technology and sustainability positions data centers as essential assets for investors seeking stability and growth in the infrastructure of tomorrow.
Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives for Data Center Investment and Growth
Zeroing in at the crossroads of traditional real estate, diversification strategies offer an attractive risk-adjusted total return profile with long-term asymmetric upside. For investors (as equity partners or strategic capital sources), data centers position themselves between predictable returns, growth opportunities, technological alignment, and sustainability, delivering on both financial and ESG objectives. As society moves increasingly digital, data centers emerge as essential infrastructure for a digital-first world. Below is a deeper dive into why investing in this space makes sense and how alignment across certain areas can offer maximum growth opportunities.